- Home
- NG Hindi
- India
- World
- Culture
- Politics
- Lifestyle
- Entertainment
- Economy
- Sex & Relationships
- Sports
- Sp. Coverage
- Misc.
- NewsGram Exclusive
- Jobs / Internships

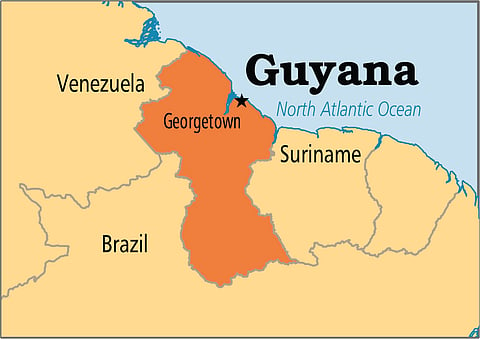
Where is Guyana?
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a sovereign state on the northern mainland of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Suriname to the east and Venezuela to the west. With 215,000 square kilometres, Guyana is the third-smallest country on mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname.
How many people of Indian origin live there?
Its current population of the country is close to 7.5 Lakh (700 thousand) and about 44 percent of Guyanese population consists of people of Indian origin. The descendants of indentured East Indian immigrants and settlers who came to British Guyana between 1838 and 1928 constitute the largest group in the population, Today, they play essential roles in the economic, political and cultural life of the country. The current Prime Minister of Guyana is of Tamil origin, Mr Moses Nagamootoo.
How did East Indians arrive in Guyana?
Three years after the start of Potuguese immigration and four months before African emanicipation in August 1838, East Indians started to arrive. Over the next nine decades, 239,909 Indian immigrants would arrive until the termination of the system in 1917, a few hundred others came up to 1928. Of these, 75,547 returned to India under the terms of their contract. The remainder who survived chose to make this country their home.
What were the first few Indian languages of Guyana?
First immigrants from India to Guyana were a form of Bhojpuri people. During that period 1842-1871, more than 73 percent of the immigrants came from areas where the languages spoken were Maithali, Magahi, Bhojpuri, Avadhi and several western dialects.
Over time in the new environment, a process of homongenization took place leading to leveled form of Bhojpuri that subsumed the other dialects. This amalgamated language was termed as "Guyanese Bhojpuri".
Why Tamil language was not subsumed by "Guyanese Bhojpuris"?
Tamil language was not subsumed by the "Guyanese Bhojpuri" as Tamil belongs to the Dravidian family of languages whereas the north Indian languages are members of the Indo Aryan family of languages. In Guyana, it is well known that in the Albion area of the country, there is a large Tamil community where the Dravidian culture still flourishes. So, South Indian immigrants learned the Guyanese Bhojpuri for communication with their north Indian counterpart but maintained communication in Tamil within their group.
How did Urdu emerge?
Around three quarters of all the Indian indentured immigrants to Guyana were Hindus and around one quarter were Muslims. This division is important as religion has played a large pole in the Indian culture that evolved in Guyana. Towards the end of indentureship period, more and more formal Hindi and Urdu were being introduced through the school system, the translators examinations and the influx of more educated immigrants to take on the role of Hindu and Muslim priests.(image: operationworld.org)(Inputs from stabroeknews.com and Ekta Mal)
